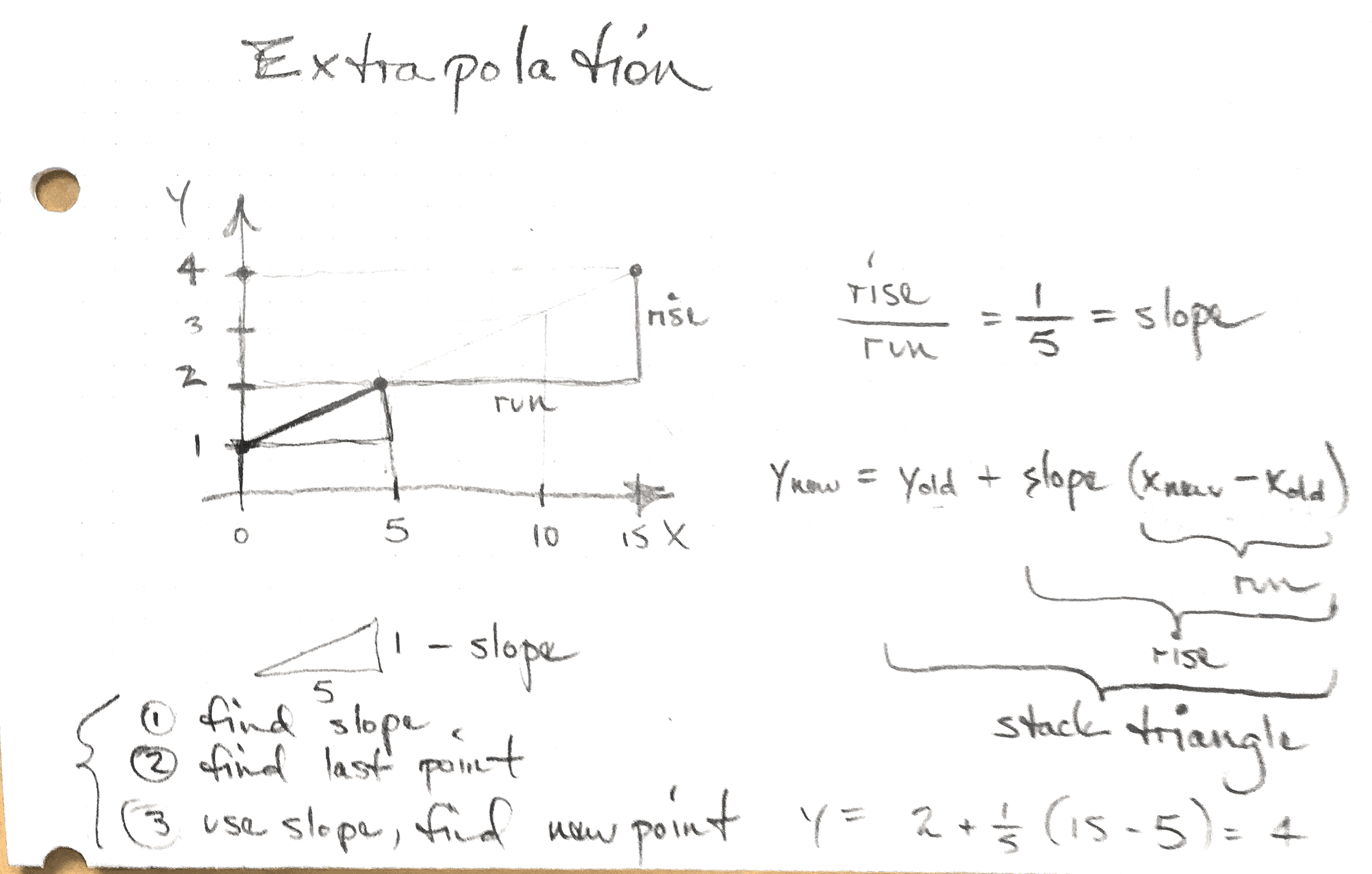
Linear Extrapolation Explained . linear extrapolation uses a subset of the data instead of the entire data set. For example, let’s say your pay increases average $200 per year. Extrapolation is a way to make guesses about the future or about some hypothetical situation based on data that you already know. You’re basically taking your “best guess”. this tutorial explains the difference between interpolation and extrapolation in statistics, including. linear extrapolation means creating a tangent line at the end of the known data and extending it beyond that limit. This is the most basic form of extrapolation that uses a linear equation to predict future outcomes. extrapolation beyond the scope of the model occurs when one uses an estimated regression equation to estimate a mean μ y or to. Linear extrapolation assumes that the trend between two known data points continues. For this type of data, it is sometimes.
from danielrsoto.com
extrapolation beyond the scope of the model occurs when one uses an estimated regression equation to estimate a mean μ y or to. For example, let’s say your pay increases average $200 per year. linear extrapolation uses a subset of the data instead of the entire data set. This is the most basic form of extrapolation that uses a linear equation to predict future outcomes. linear extrapolation means creating a tangent line at the end of the known data and extending it beyond that limit. For this type of data, it is sometimes. Linear extrapolation assumes that the trend between two known data points continues. You’re basically taking your “best guess”. Extrapolation is a way to make guesses about the future or about some hypothetical situation based on data that you already know. this tutorial explains the difference between interpolation and extrapolation in statistics, including.
Extrapolations and Fits Quantitative Methods Course Notes
Linear Extrapolation Explained Linear extrapolation assumes that the trend between two known data points continues. linear extrapolation uses a subset of the data instead of the entire data set. Extrapolation is a way to make guesses about the future or about some hypothetical situation based on data that you already know. Linear extrapolation assumes that the trend between two known data points continues. You’re basically taking your “best guess”. linear extrapolation means creating a tangent line at the end of the known data and extending it beyond that limit. For this type of data, it is sometimes. extrapolation beyond the scope of the model occurs when one uses an estimated regression equation to estimate a mean μ y or to. This is the most basic form of extrapolation that uses a linear equation to predict future outcomes. this tutorial explains the difference between interpolation and extrapolation in statistics, including. For example, let’s say your pay increases average $200 per year.
From www.researchgate.net
1 Linear and power model extrapolation methods compared to actual... Download Scientific Diagram Linear Extrapolation Explained linear extrapolation uses a subset of the data instead of the entire data set. this tutorial explains the difference between interpolation and extrapolation in statistics, including. extrapolation beyond the scope of the model occurs when one uses an estimated regression equation to estimate a mean μ y or to. For example, let’s say your pay increases average $200. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Interpolation, extrapolation and regression PowerPoint Presentation ID5273285 Linear Extrapolation Explained linear extrapolation means creating a tangent line at the end of the known data and extending it beyond that limit. this tutorial explains the difference between interpolation and extrapolation in statistics, including. For example, let’s say your pay increases average $200 per year. For this type of data, it is sometimes. Extrapolation is a way to make guesses. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From tapintoteenminds.com
Visualizing Two Variable Linear and Relationships Linear Extrapolation Explained You’re basically taking your “best guess”. this tutorial explains the difference between interpolation and extrapolation in statistics, including. linear extrapolation means creating a tangent line at the end of the known data and extending it beyond that limit. This is the most basic form of extrapolation that uses a linear equation to predict future outcomes. extrapolation beyond the. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Use linear extrapolation and the information below to Linear Extrapolation Explained linear extrapolation means creating a tangent line at the end of the known data and extending it beyond that limit. Extrapolation is a way to make guesses about the future or about some hypothetical situation based on data that you already know. This is the most basic form of extrapolation that uses a linear equation to predict future outcomes.. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From www.youtube.com
Interpolation And Extrapolation YouTube Linear Extrapolation Explained This is the most basic form of extrapolation that uses a linear equation to predict future outcomes. For example, let’s say your pay increases average $200 per year. extrapolation beyond the scope of the model occurs when one uses an estimated regression equation to estimate a mean μ y or to. For this type of data, it is sometimes. You’re. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From www.researchgate.net
18 Threshold voltage extraction using the linear extrapolation method. Download Scientific Linear Extrapolation Explained linear extrapolation means creating a tangent line at the end of the known data and extending it beyond that limit. extrapolation beyond the scope of the model occurs when one uses an estimated regression equation to estimate a mean μ y or to. linear extrapolation uses a subset of the data instead of the entire data set. This. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From www.researchgate.net
Linear extrapolation between two parents to find the new child's... Download Scientific Diagram Linear Extrapolation Explained Extrapolation is a way to make guesses about the future or about some hypothetical situation based on data that you already know. This is the most basic form of extrapolation that uses a linear equation to predict future outcomes. For example, let’s say your pay increases average $200 per year. this tutorial explains the difference between interpolation and extrapolation. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From www.studocu.com
Extrapolation Formula in mathematics Extrapolation Formula Let us consider the two endpoints Linear Extrapolation Explained Extrapolation is a way to make guesses about the future or about some hypothetical situation based on data that you already know. You’re basically taking your “best guess”. For this type of data, it is sometimes. extrapolation beyond the scope of the model occurs when one uses an estimated regression equation to estimate a mean μ y or to. For. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From www.researchgate.net
LinearNonThreshold (LNT) model and uncertainties in extrapolation of... Download Scientific Linear Extrapolation Explained Extrapolation is a way to make guesses about the future or about some hypothetical situation based on data that you already know. For example, let’s say your pay increases average $200 per year. extrapolation beyond the scope of the model occurs when one uses an estimated regression equation to estimate a mean μ y or to. linear extrapolation means. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From danielrsoto.com
Extrapolations and Fits Quantitative Methods Course Notes Linear Extrapolation Explained linear extrapolation uses a subset of the data instead of the entire data set. Extrapolation is a way to make guesses about the future or about some hypothetical situation based on data that you already know. Linear extrapolation assumes that the trend between two known data points continues. For example, let’s say your pay increases average $200 per year.. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From www.perfmatrix.com
Linear Extrapolation Calculator Performance Testing Linear Extrapolation Explained linear extrapolation uses a subset of the data instead of the entire data set. this tutorial explains the difference between interpolation and extrapolation in statistics, including. Extrapolation is a way to make guesses about the future or about some hypothetical situation based on data that you already know. linear extrapolation means creating a tangent line at the. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From www.researchgate.net
3 Illustration of the linear extrapolation schemes for the LK group... Download Scientific Linear Extrapolation Explained This is the most basic form of extrapolation that uses a linear equation to predict future outcomes. linear extrapolation uses a subset of the data instead of the entire data set. linear extrapolation means creating a tangent line at the end of the known data and extending it beyond that limit. this tutorial explains the difference between. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From www.upgrad.com
Linear Regression Revision upGrad Learn Linear Extrapolation Explained Linear extrapolation assumes that the trend between two known data points continues. For example, let’s say your pay increases average $200 per year. linear extrapolation means creating a tangent line at the end of the known data and extending it beyond that limit. This is the most basic form of extrapolation that uses a linear equation to predict future. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From www.youtube.com
The Extrapolation Formula YouTube Linear Extrapolation Explained this tutorial explains the difference between interpolation and extrapolation in statistics, including. linear extrapolation means creating a tangent line at the end of the known data and extending it beyond that limit. You’re basically taking your “best guess”. For example, let’s say your pay increases average $200 per year. This is the most basic form of extrapolation that. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From www.researchgate.net
Systematic Forecasting Error of Linear Extrapolation Download Scientific Diagram Linear Extrapolation Explained Extrapolation is a way to make guesses about the future or about some hypothetical situation based on data that you already know. Linear extrapolation assumes that the trend between two known data points continues. linear extrapolation uses a subset of the data instead of the entire data set. For this type of data, it is sometimes. this tutorial. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From www.researchgate.net
Illustration of the linear extrapolation (a) and second derivative (b)... Download Scientific Linear Extrapolation Explained For this type of data, it is sometimes. Extrapolation is a way to make guesses about the future or about some hypothetical situation based on data that you already know. Linear extrapolation assumes that the trend between two known data points continues. this tutorial explains the difference between interpolation and extrapolation in statistics, including. extrapolation beyond the scope of. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From www.researchgate.net
Extrapolation using Linear Regression Download Scientific Diagram Linear Extrapolation Explained For example, let’s say your pay increases average $200 per year. linear extrapolation means creating a tangent line at the end of the known data and extending it beyond that limit. Extrapolation is a way to make guesses about the future or about some hypothetical situation based on data that you already know. this tutorial explains the difference. Linear Extrapolation Explained.
From www.researchgate.net
Linear extrapolation in 1/D for the C 4v symmetric U(1) iPEPS Ansatz... Download Scientific Linear Extrapolation Explained Extrapolation is a way to make guesses about the future or about some hypothetical situation based on data that you already know. You’re basically taking your “best guess”. linear extrapolation uses a subset of the data instead of the entire data set. this tutorial explains the difference between interpolation and extrapolation in statistics, including. This is the most. Linear Extrapolation Explained.